What is Credential Harvesting and how does it work?
Written by NDIT Cyber Threat Intelligence Team
Credential harvesting is a type of malicious activity where threat actors steal login information, such as usernames and passwords, from unsuspecting victims. This attack is most often achieved through phishing email lures and fake login pages.
Within minutes of attackers obtaining these stolen credentials they will attempt to gain access to personal accounts or corporate systems.

Credential harvesting provides attackers with initial access, enabling them to potentially steal sensitive information, establish remote access, deliver malware, and potentially escalate to more damaging attacks like ransomware.
Credential harvesting is particularly dangerous because it can go unnoticed for long periods, providing attackers access over prolonged periods. Credential harvesting becomes even more dangerous when individuals and organizations reuse the same password across multiple accounts or platforms, giving threat actors the opportunity to access those accounts as well.
Examples of Credential Harvesting
Credential harvesting is most often observed starting with a phishing email that is offering to view an important document. Threat actors will often leverage legitimate hosting services or compromised cloud environments to serve as the first step of delivery. This decreases the chance of a user detecting the phish and lowers their suspicion of the URL contained in the phishing email.
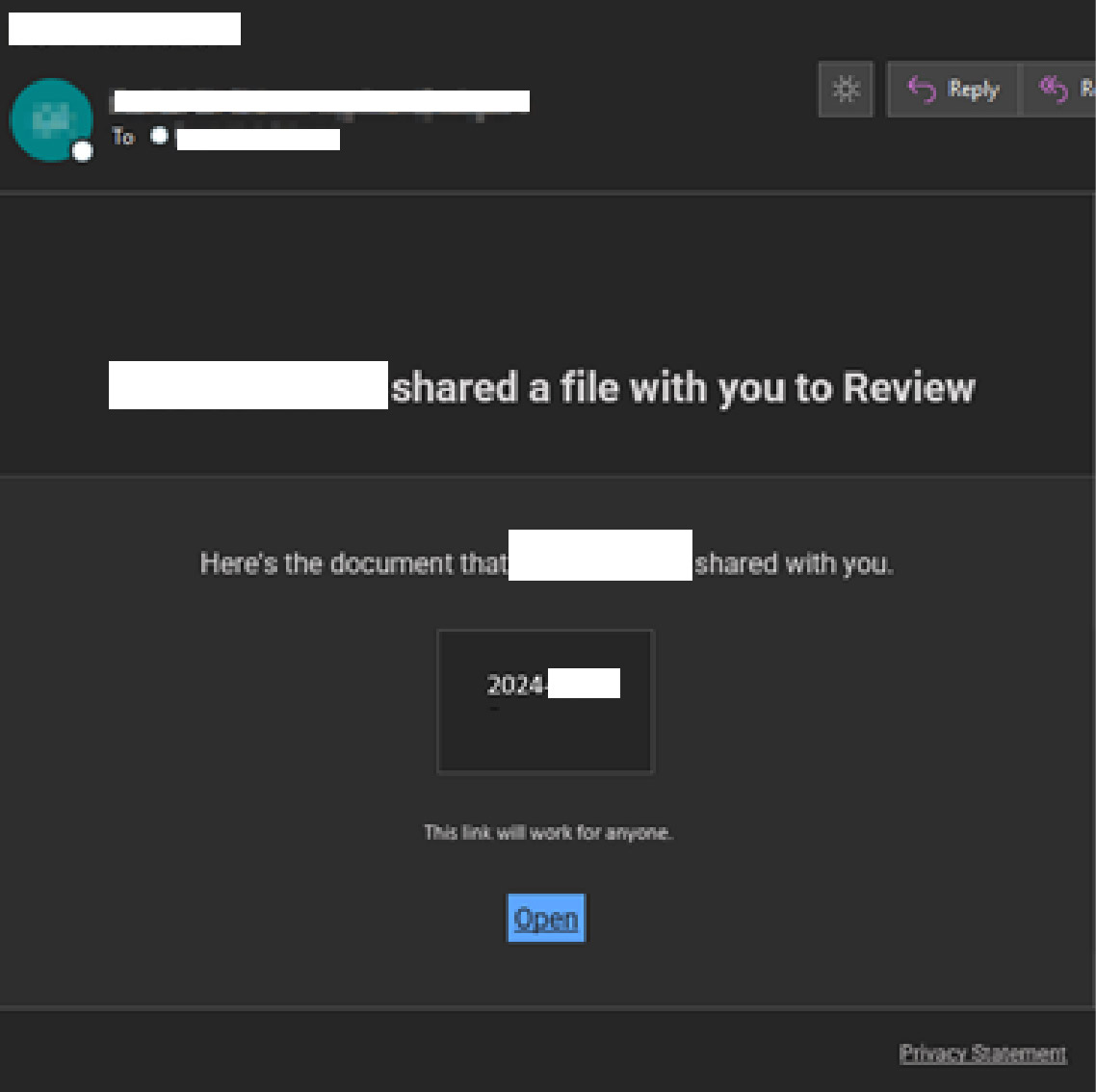
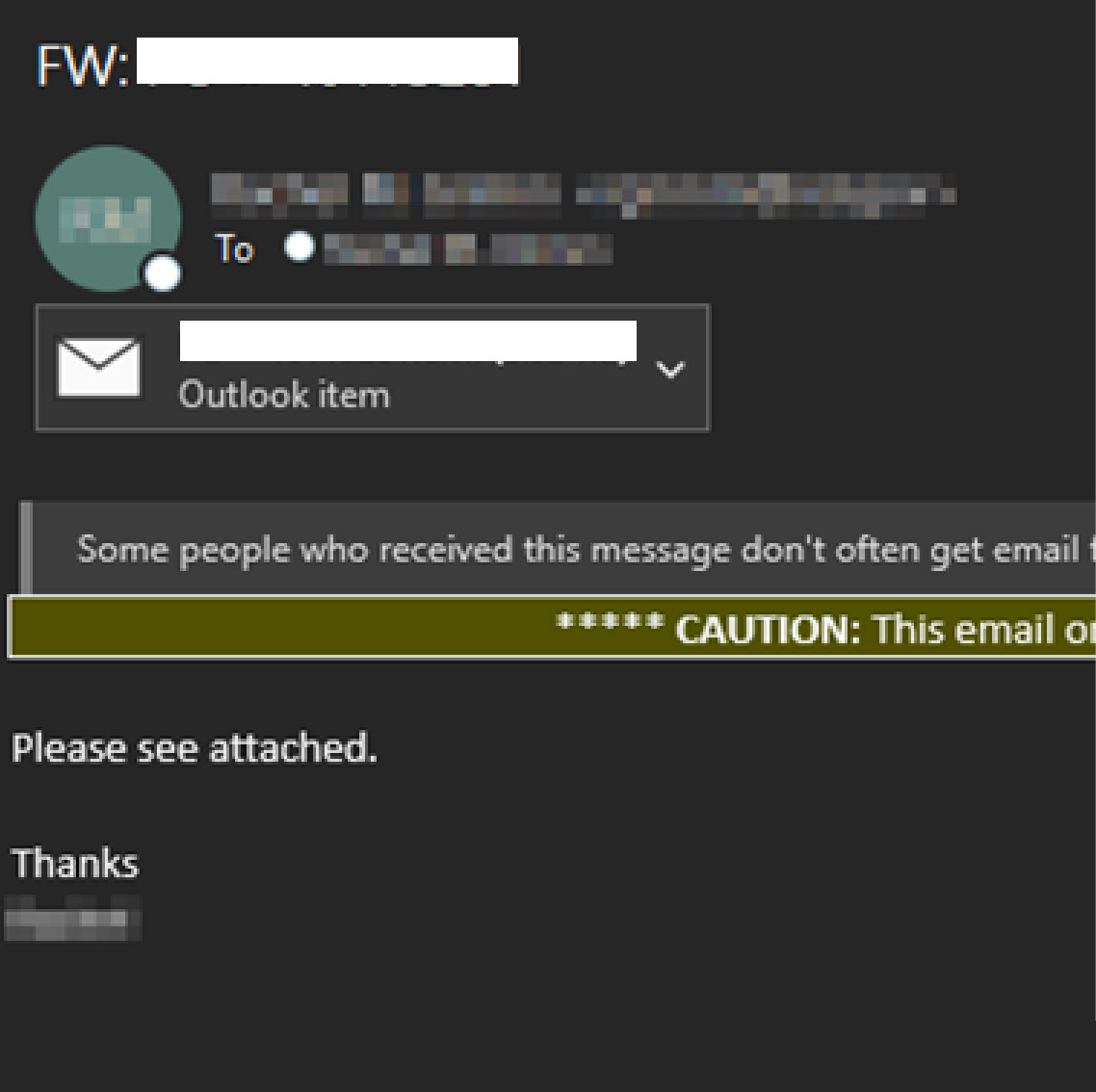
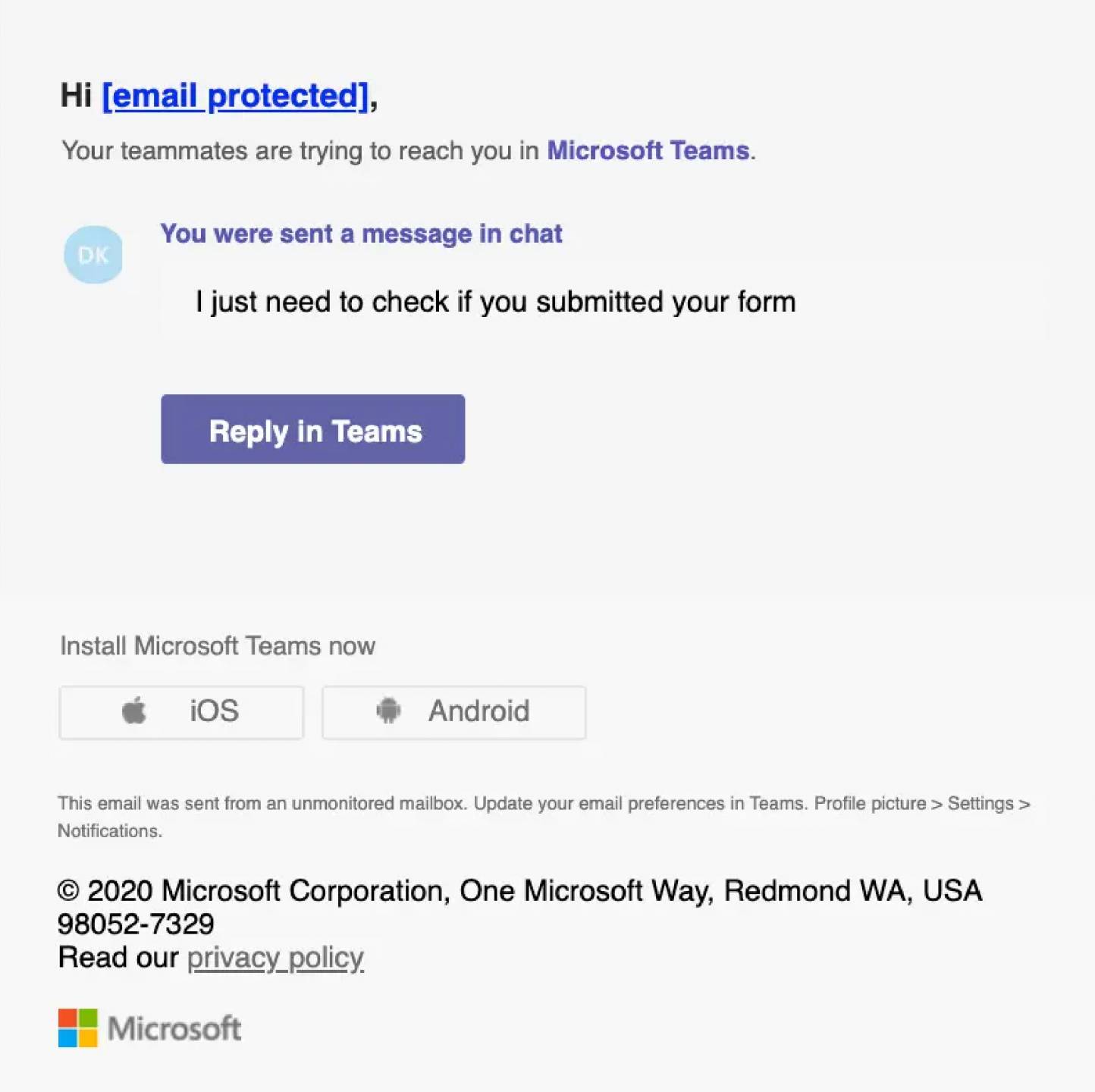
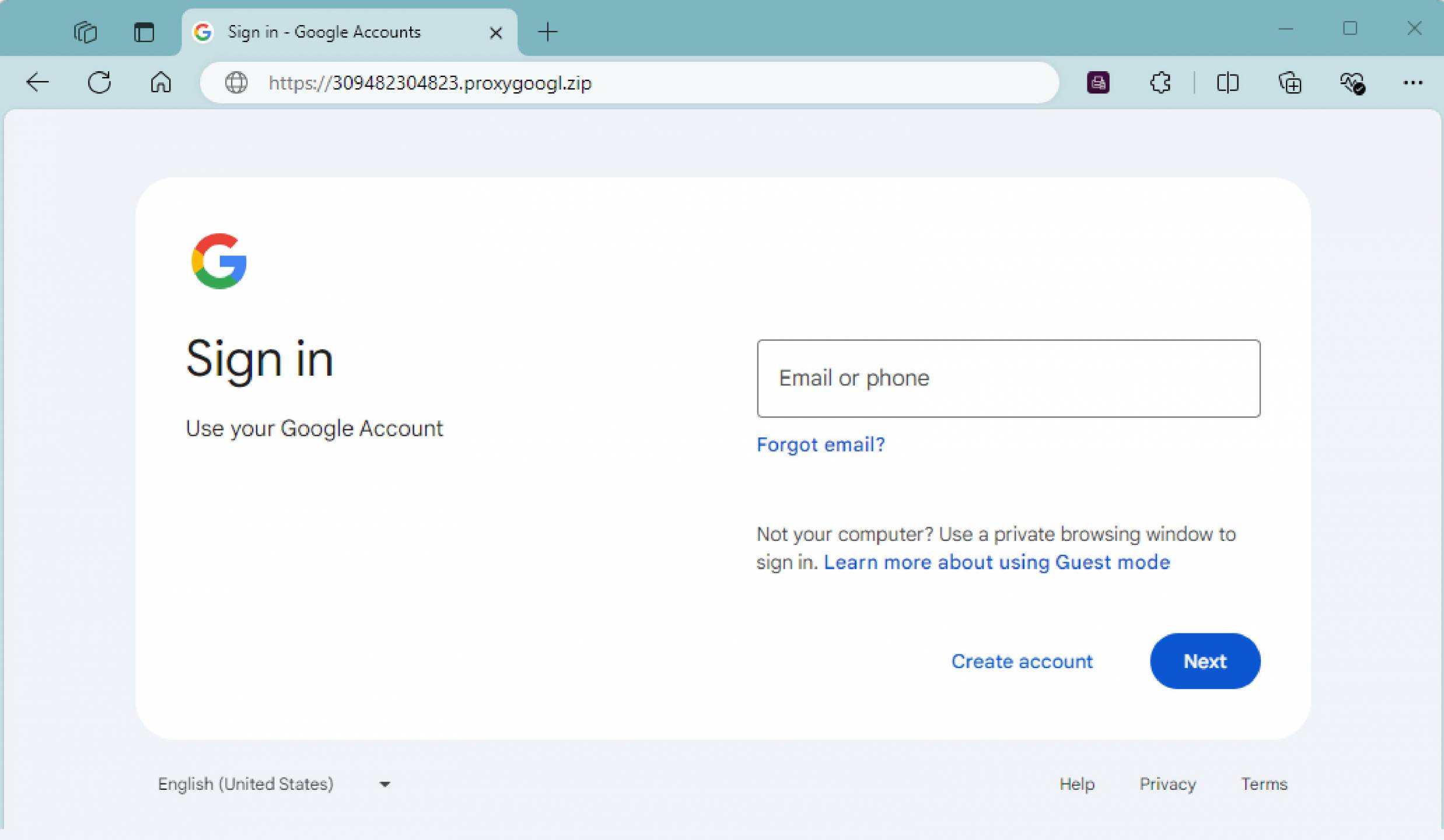
The URL in the phishing email is designed to redirect the user to a fake login page impersonating legitimate services such as Microsoft or Google. Once the victim has navigated from the URL contained in the phishing email, they are generally presented something that appears to be an inaccessible document that they must login to view.

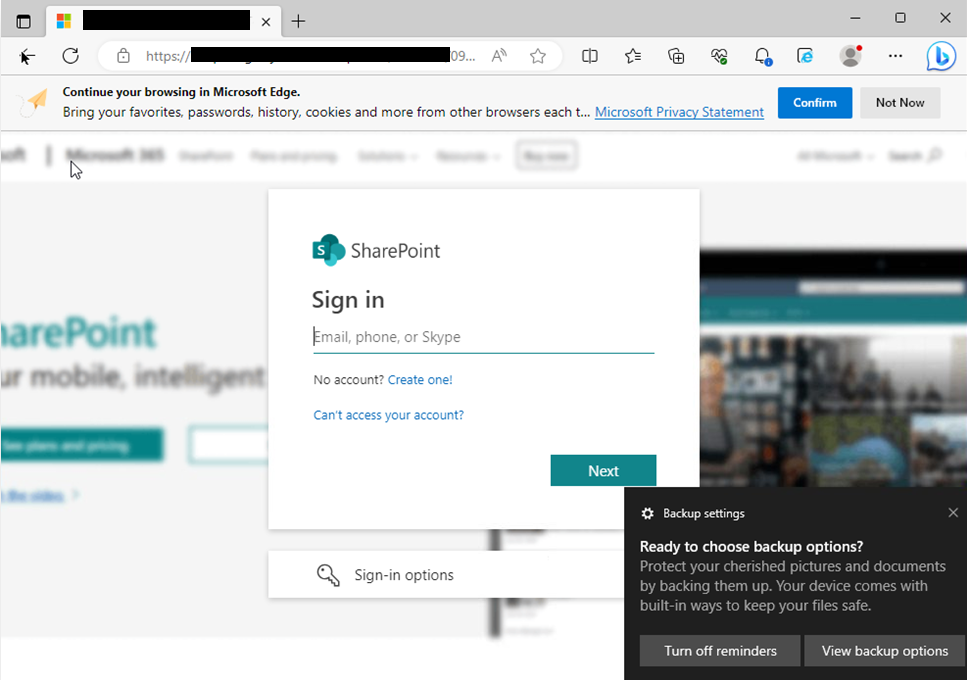
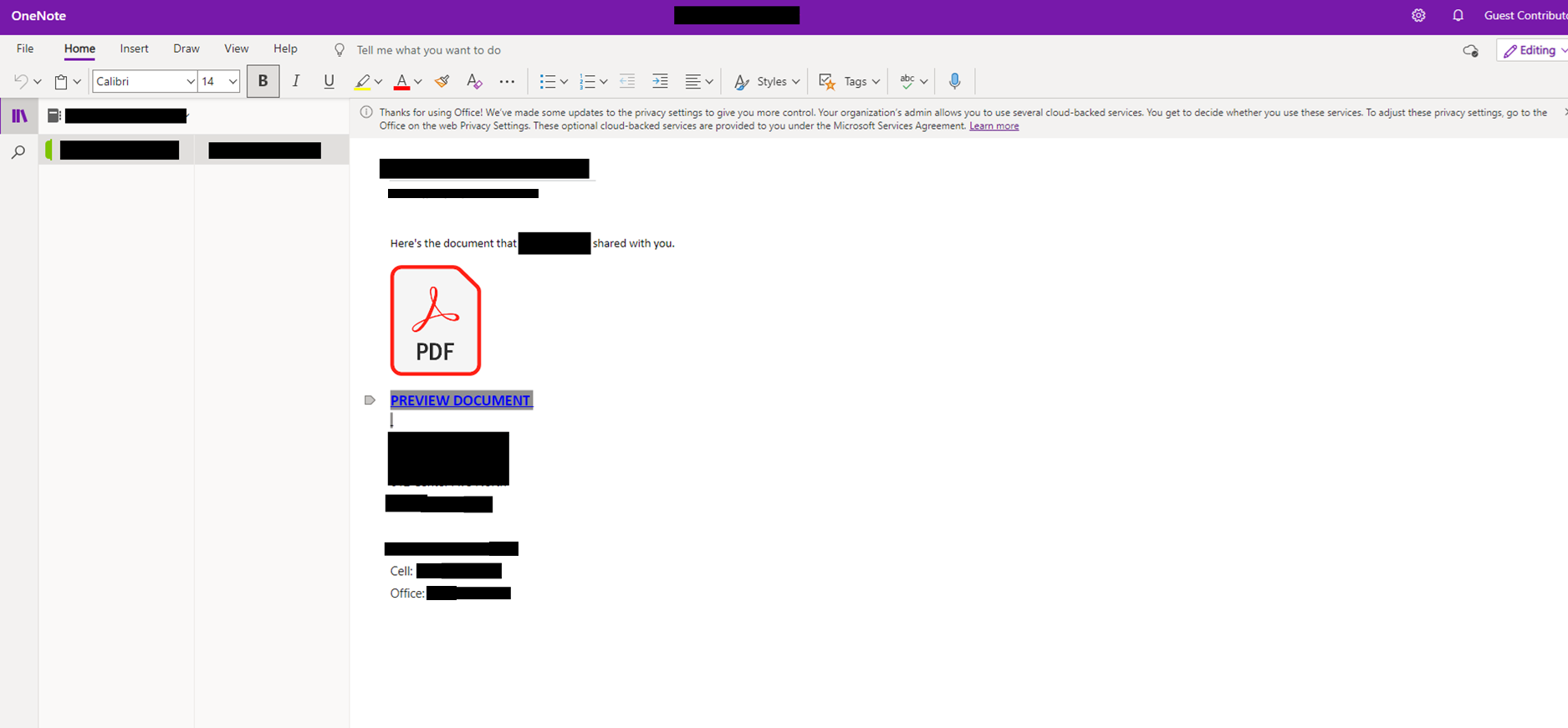
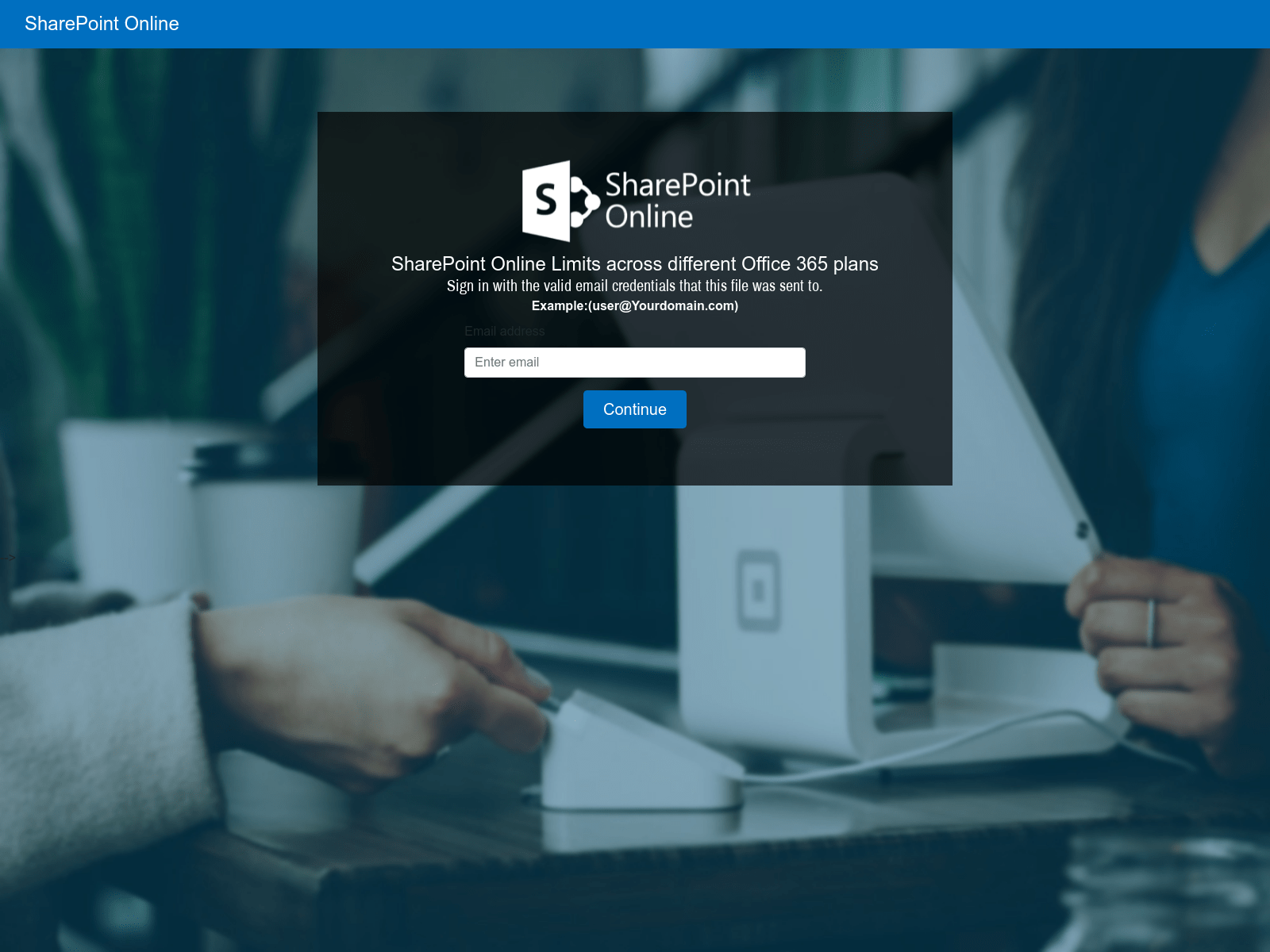
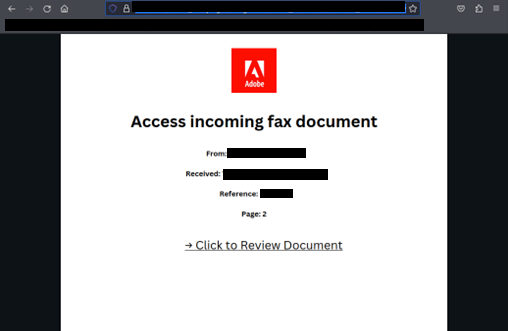
The final phase of the attack is presenting a fraudulent login screen that appears to be for a service like Microsoft or Google. Any credentials (username and password) entered into these pages will be stolen by the attacker.
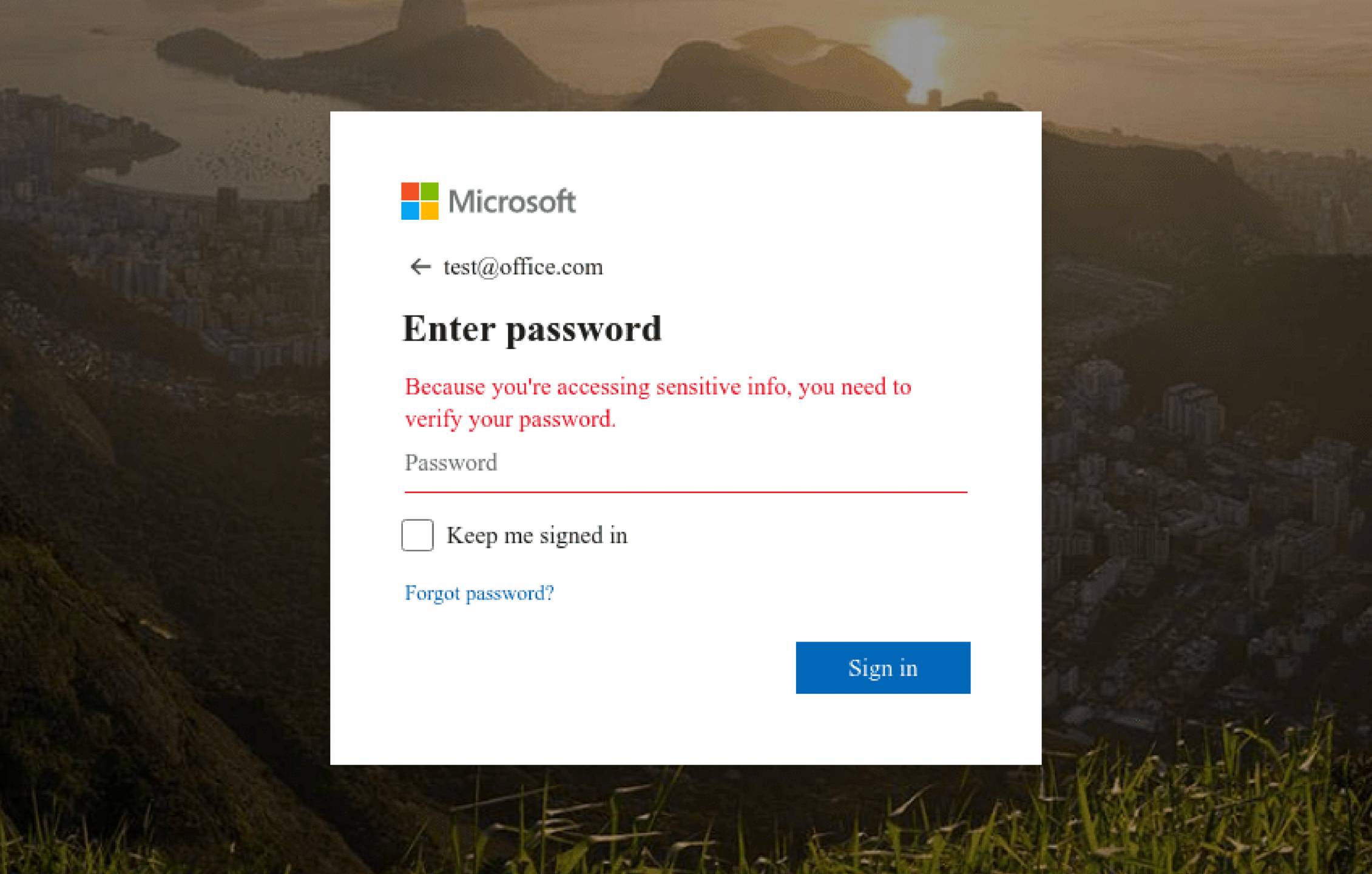
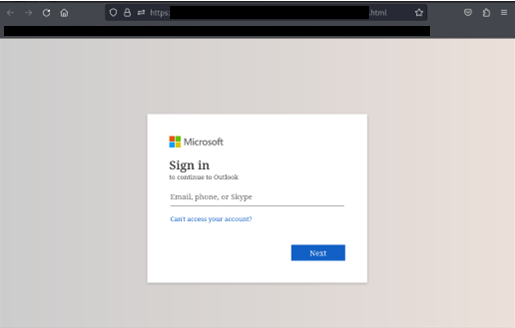
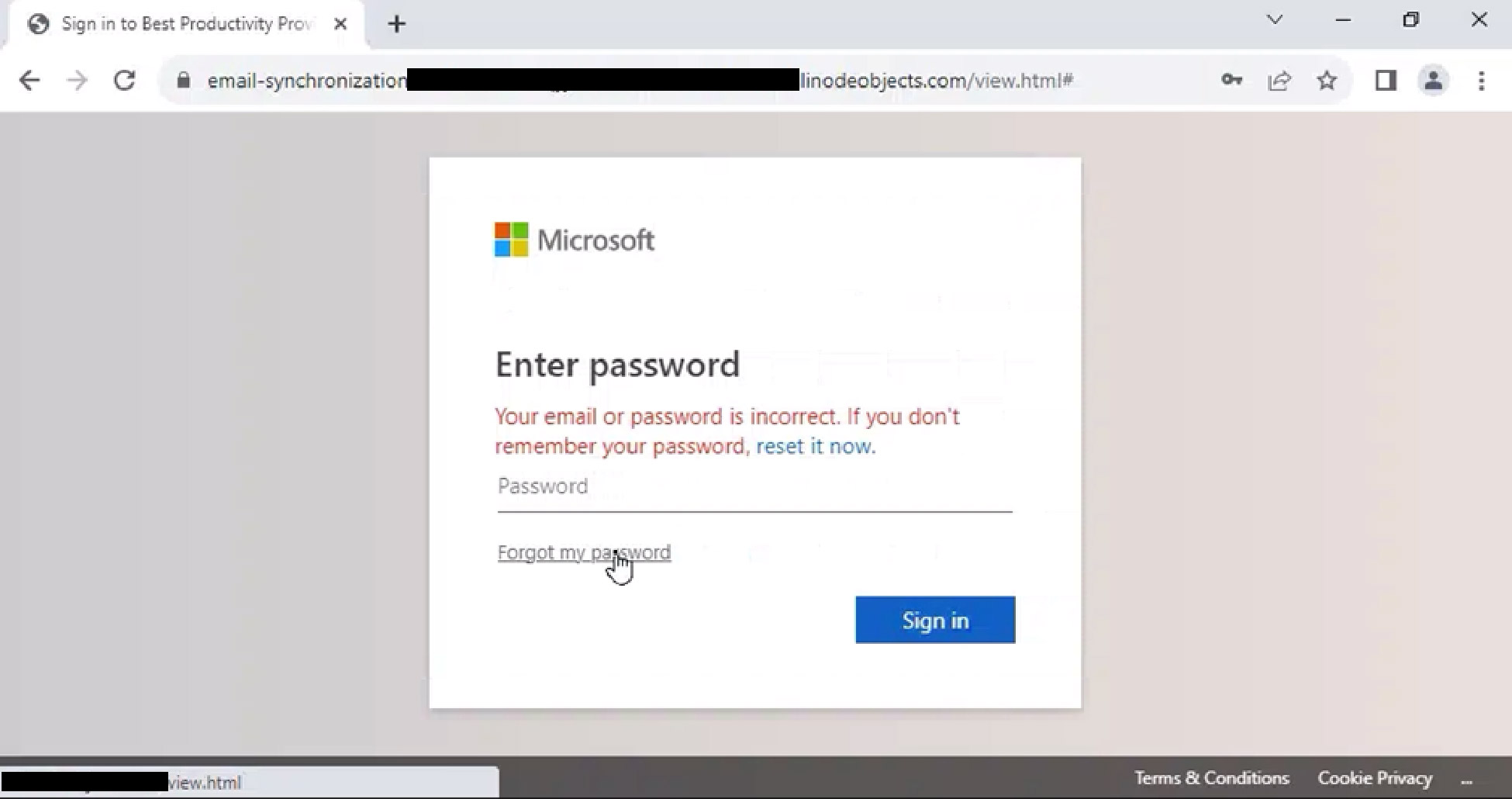
This is an example of a potential google credential harvester. A user should pay attention when the domain or URL does not seem to match what should be expected.
How can I protect myself or my company?
Educate Yourself and Your Employees
To educate yourself and your employees about credential harvesting, start by offering regular security awareness training that focuses on common attack methods like credential harvesting campaigns and what threat actors are attempting to gain from this tactic.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication
The single most effective method to defend against credential harvesting is multi-factor or two-factor authentication. This helps deny attackers the successful use of any stolen credentials.
Response
If you suspect you've fallen victim to a credential harvesting campaign the first step is to immediately change the passwords for all affected accounts, ensuring that you don't reuse the same password across different accounts. Next, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) if it’s not already in place. Finally, monitor your accounts for any suspicious activity and promptly report any unauthorized actions.
