Executive Summary

In the government sector, we face continual challenges and opportunities in how we leverage technology to serve citizens. As we emerge from a world flush with technological advancement brought on by our government response to the fading COVID-19 pandemic, the state seeks to capitalize on those investments to further empower people, improve lives, and inspire success throughout the 2023-2025 biennium.
For the 2023-2025 biennium, North Dakota Information Technology will seek to make improvements across four macro areas:
- Closing Workforce Gaps
- Enabling Decision Making
- Managing Risk
- Citizen and Business Engagement
What this means for North Dakota's technology efforts is described below in this strategic plan. Additionally, the related objectives and accomplishments that are implemented as a part of these four strategic themes may be viewed as part of the greater Statewide IT Plan and that plan's related dashboard of information.
As we move toward understanding what the "new normal" truly is, technology continues to be the backbone that supports much of what we do. Whether it is improving Main Street, supporting public health, transforming education, improving tribal partnerships, or reinventing government, technology is at the core of making sure the business -- and the people that run the business -- can function.
As NDIT "works as one" with legislative partners and other stakeholders, we will relentlessly move closer to our goal of delivering on our strategic themes for the next biennium.
Shawn Riley,
CIO
Efficiency and Effectiveness of NDIT
In order to maintain and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of processes and the provision of technology services, NDIT utilizes a seven-step cycle for developing goals, strategies and activities, and for executing and maintaining the initiatives that support strategic delivery:
1. Listen
All efforts start with listening to our stakeholders to understand what they need, how they need it, and what we need to do to meet their expectations. To better understand this, NDIT utilizes roles and processes from within its Customer Success Office to collaborating with business units in determining and prioritizing IT needs.
2. Assess
A key component of self-improvement is understanding your strengths and weaknesses. And for any organization, improvement also includes understanding the current state of its strategies and tactics, and how those are currently supporting the global vision. In IT, how strong or weak an organization is in any key discipline can be defined using a “Capability Maturity Model.” NDIT utilizes an operational maturity baseline that was established in 2017, and compares progress made against it by leveraging semi-annual IT satisfaction surveys.
3. Envision
Once we understand what is needed of us, and what the maturity level of our capabilities are, we need to envision what we should become. NDIT's current vision is, “How might we provide world class technology and service?” By phrasing our vision as a question, we are always asking ourselves how we can do better.
4. Strategize
Strategy setting is the next step in the efficiency and effectiveness process for NDIT, and it includes the development of goals and objectives that will help the organization realize its long-term value. See below for more information on what NDIT has planned for 2023-2025.
5. Deploy Tactics
Tactical planning translates broad strategies into specific initiatives that help improve the organization. At NDIT, management utilizes the Objective-Key Results, or OKR method, to regularly review strategies, prioritize initiatives, and either start, stop, or continue those initiatives depending on how they currently align to the state’s IT goals. This is done on a quarterly cycle to ensure timely adaptation to evolving customer needs and technological advancements.
6. Manage Logistics
Logistics is the detailed organization and implementation of a complex operation. At any given time NDIT is working on numerous activities to move us toward our vision of becoming and sustaining ourselves as a world class IT organization. Delivering on these initiatives requires the coordination of stakeholders across many lines of business belonging to numerous, disparate groups. NDIT leverages various IT Governance and IT Management processes to ensure teams work together to deliver unified outcomes. Examples include the IT Coordinators Council, the State IT Advisory Committee, and various Enterprise (IT) Architecture teams.
7. Maintain Operations
At the operations level, NDIT staff employ a myriad of sub-processes to ensure initiatives are sustained over the long term. Operations staff ensure that network infrastructure, servers and other devices are available and secure; that everyone’s workstations are functioning; and that all issues related to any IT system are escalated to the right teams for resolution in an efficient manner.
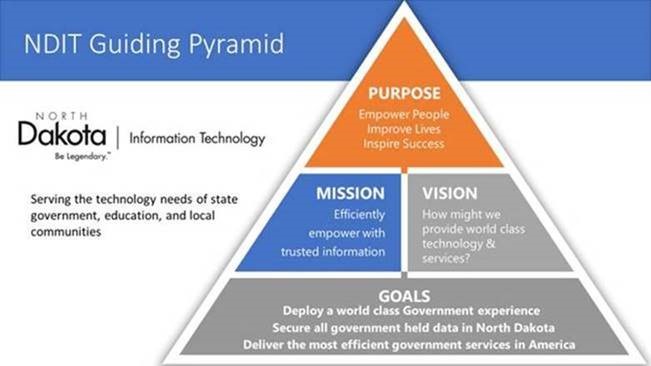
Purpose, Mission, Vision, Goals
We leverage our Strategic Pyramid (see image) to show the interconnectedness of our organization's primary directives. We follow these guiding principles as we analyze business and IT information (gathered through a series of strategic sessions conducted with state agencies) to determine the key themes that will help the state continually position itself as a world class, secure, and efficient technology entity.
NDIT Strategic Themes for 2023-2025
1. Closing Workforce Gaps
Workforce gaps are here, and they will only get worse in the coming years. The harsh reality of ongoing retirements and the highly competitive nature of the job market means that as a state we will need to rely on various forms of automation and modernization to continue to be able to serve our citizens with the available human workforce. This theme focuses on leveraging technology that would allow agency staff to reduce time spent on mundane or non-productive activities, and also to make many general office tasks easier. New or existing technologies within this theme to either implement or expand upon include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Conversational AI (chatbots, computer-based interaction with humans)
- Machine Learning (computer creates rules and predictions based on facts, self-learning)
- Automation (removing commodity, repeating, predictable, mundane, boring work)
- Knowledge management
- Organizing, creating, using, and sharing information in the organization
- Lowering the pain of turnover and attrition
- Retaining knowledge
- Paper to Electronic to Digital
- Streamlining input, services, workflows, searchability, and management of data
- Eliminating data entry and enabling artificial intelligence
- Processing the creation, maintenance, and archiving of documents
- Tech debt remediation and push to mobile interfaces and apps
- Eliminating technology that is no longer supportable in the workforce (e.g., mainframe)
- Eliminating technology that is not commonly taught or learned
- Eliminating technology that is no longer used, causes manual work, or inhibits digital
2. Enabling Decision Making
Many state jobs require us to make decisions that have a direct impact on ND citizens. How we analyze and respond to various events and information affects state policy, which may have an impact that lasts for decades. Technology projects and solutions in this theme are related to ensuring state staff have access to as many key data points as is possible – so the best decisions may be made, and so staff can focus on the data itself instead of trying to figure out how to get it. New or existing technologies within this theme to either implement or expand upon include:
- Data Accessibility
- Easy access of data from all operational systems
- Easy data reporting and visualization on any endpoint (mobile device, laptop, etc.)
- Data Fabric
- Standardized architecture for data input, storage, and processing of data
- Driven by application programming interface (API) connectivity
- Specialized data lakes and warehouses for data domains and/or agencies
- Data Governance
- Defined ownership and management of data
- Secure and auditable data
- Data is defined and quality is managed
3. Managing Risk
This theme is focused on ensuring that the risk of having state systems and information breached by a “bad actor” is minimized to the greatest extent possible. New or existing technologies within this theme to either implement or expand upon include:
- Universal Vulnerability Management
- Vulnerabilities identified and remediated for every device on the state's network
- Easy reporting and visibility to all vulnerabilities
- Simple patching across all device types
- All endpoints on the state's network are protected
- Governance Risk and Compliance
- Statewide risk management framework
- Third party risk management
- Capital Risk
- Statewide project and portfolio management
- Small to Medium projects risk managed
4. Citizen and Business Engagement
Ensuring ease of access to, and ease of use of, state systems is the core of the citizen and business engagement theme. Projects to support this effort could include work toward having state services, and access to those services, further packaged into a one-stop-shop. New or existing technologies within this theme to either implement or expand upon include:
- Single location for accessing ND State Government
- Single Identity for citizens, business, and entity
- Accessible via any internet web browser or mobile app
- Citizen Relationship Management
- Universal-to-government citizen persona
- Standardized business processes enablement (e.g., for credit card processing)
Objectives and Accomplishments
The related objectives and accomplishments that are implemented as a part of these strategic themes may be viewed as part of the greater Statewide IT Plan and that plan's related dashboard of information.
